Archive for May 2023
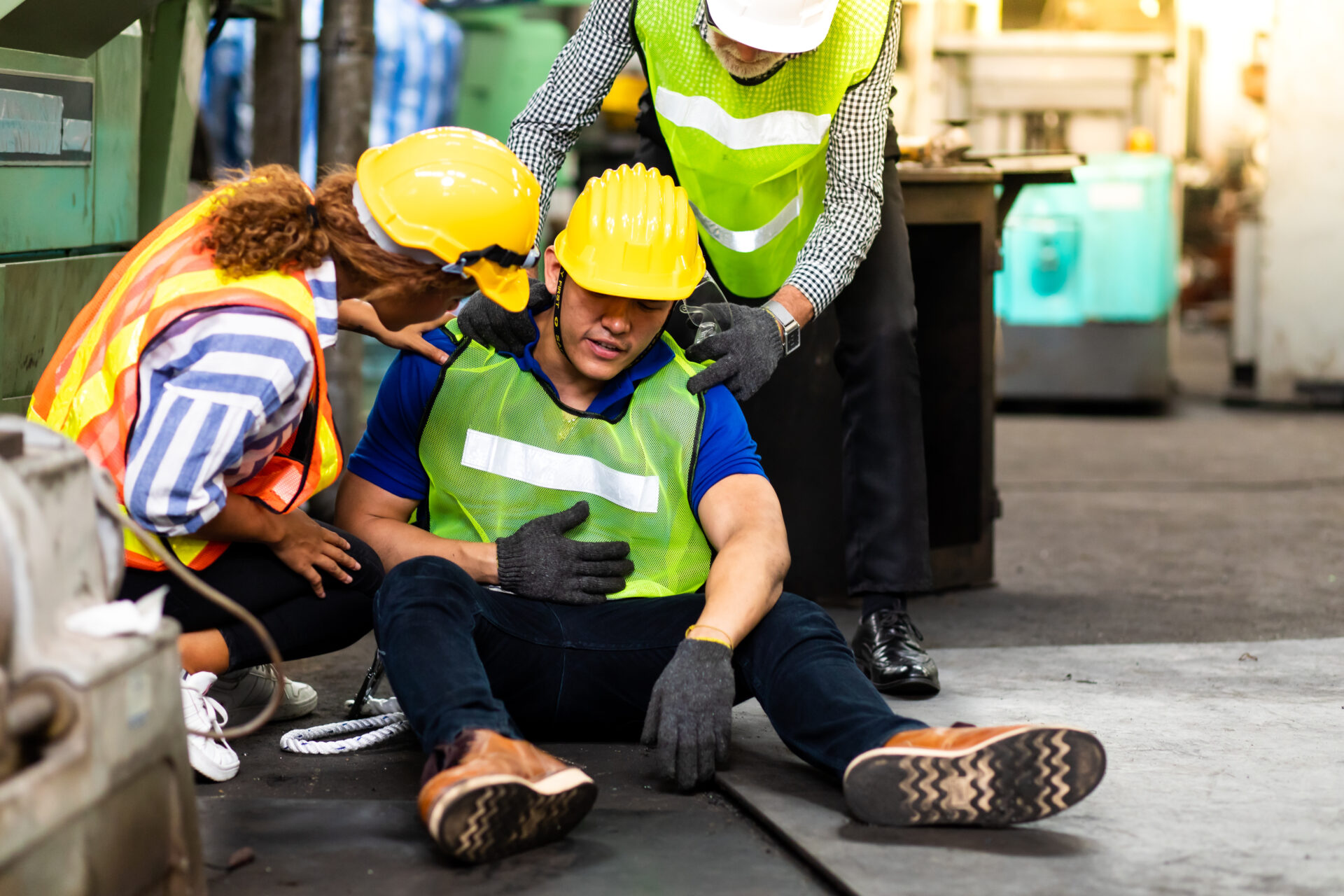
Work Injuries
When a patient visits their chiropractor due to a work injury, the chiropractor routinely looks beyond the actual injury and addresses concerns about their station setup, whether they use ergonomically correct equipment, and whether they utilize proper work techniques. The goal is both to help relieve your pain and determine how to avoid what caused it in the first place. Work injuries can occur in a variety of different work environments including construction sites, offices, warehouses, and retail stores. Much of the time, the causes of pain in the workplace include:
- Falls caused by Overexertion
- Improper lifting
- Repetitive strain
- Blunt force trauma
- Exposure to Chemicals
- Burns
Most workplace injuries are the result of soft tissue and joint damage. Improper lifting techniques are one of the most common reasons for the occurrences of pain in the workplace. You may consider visiting a chiropractor if you are experiencing any of the following pains due to your workplace injuries or otherwise:
- Back injuries (sprains, strains, disc problems)
- Neck injuries (sprains, strains, joint dysfunction)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Headache (caused by muscle tension, joint dysfunction, or poor posture)
- Numbness and tingling of extremities.
Whiplash
Describing a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck. Cervical acceleration-deceleration” (CAD) describes the mechanism of the injury, while the term “whiplash-associated disorders” (WAD) describes the injury and symptoms.
Anatomy
There are four phases that occur during “whiplash”:
- Initial position (before the collision),
- retraction
- extension
- rebound
In the initial position, there is no force on the neck due to inertia keeping it stable. Anterior longitudinal ligament injuries in whiplash may lead to cervical instability. They explain that during the retraction phase that is when the actual “whiplash” occurs since there is an unusual loading of soft tissues. The next phase is the extension, the whole neck and head switch to extension, and it is stopped or limited by the head restraint. The rebound phase transpires as a result of the phases that are mentioned.
During the refraction phase, the spine forms an S-Shaped curve, and this is caused by the flexion in the upper planes and hyperextension at the lower planes and this exceeds their physiological limits this phase the injuries occur to the lower cervical vertebrae. At the extension phase, all cervical vertebrae and the head are fully extended but do not surpass their physiological limits. Most of the injuries happen in C-5 and C-6.
Symptoms
Symptoms reported by sufferers include: pain and aching to the neck and back, referred pain to the shoulders, sensory disturbance (such as pins and needles) to the arms and legs, and headaches. Symptoms can appear directly after the injury but often are not felt until days afterward. Whiplash is usually confined to the spine. The most common areas of the spine affected by whiplash are the neck and middle of the spine. “Neck” pain is very common between the shoulder and the neck.
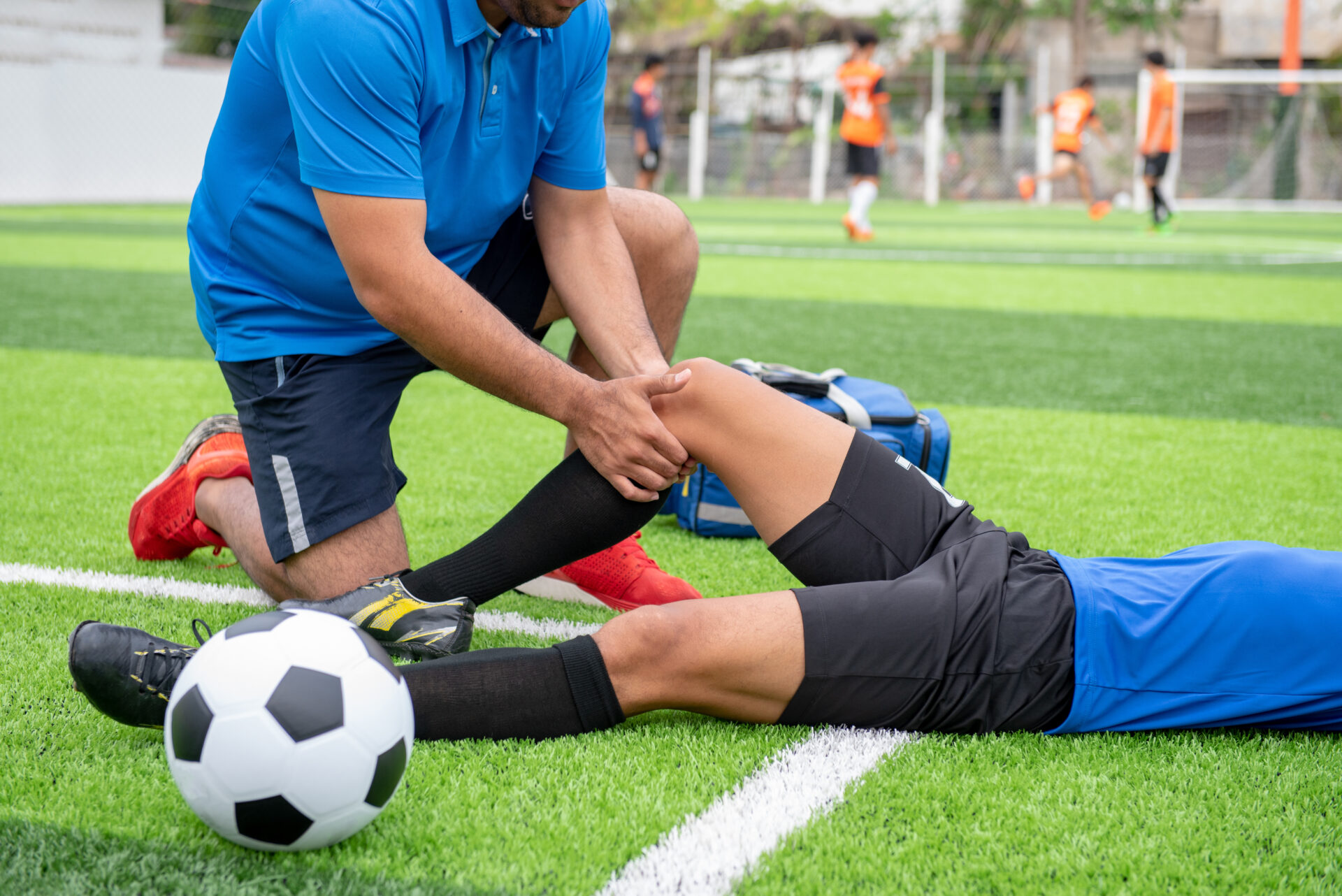
Sports Injuries
Sports injuries are injuries that occur in athletic activities. They can result from acute trauma, or from overuse of a particular body part.
Classification
Traumatic injuries account for most injuries in contact sports such as Ice Hockey, Association football, rugby league, rugby union, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, and American football because of the dynamic and high-collision nature of these sports.[citation needed] Collisions with the ground, objects, and other players are common, and unexpected dynamic forces on limbs and joints can cause injury.
Traumatic injuries can include:
- Contusion or bruise – damage to small blood vessels which causes bleeding within the tissues.
- Strain – trauma to a muscle due to overstretching and tearing of muscle fibers
- Sprain – an injury in a joint, caused by the ligament being stretched beyond its own capacity
- Wound – abrasion or puncture of the skin
- Bone fracture
- Head injury
- Spinal cord injury
In sports medicine, a catastrophic injury is defined as severe trauma to the human head, spine, or brain.
Concussions in sports became a major issue in the United States in the 2000s, as evidence connected repeated concussions with chronic traumatic encephalopathy and increased suicide risk.
Overuse and repetitive stress injury problems associated with sports include:
- Runner’s knee
- Tennis elbow
- Tendinosis
Some activities have particular risks:
- Bicycle safety
- Gun safety
- Sailing ship accidents
- Skateboarding
Soft tissue injuries
When soft tissue experiences trauma, the dead and damaged cells release chemicals, which initiate an inflammatory response. Inflammation is characterized by pain, localized swelling, heat, redness and a loss of function. Small blood vessels are damaged and opened up, producing bleeding within the tissue. In the body’s normal reaction, a small blood clot is formed in order to stop this bleeding and from this clot special cells (called fibroblasts) begin the healing process by laying down scar tissue.
The inflammatory stage is therefore the first phase of healing. However, too much of an inflammatory response in the early stage can mean that the healing process takes longer and a return to activity is delayed. Sports injury treatments are intended to minimize the inflammatory phase of an injury so that the overall healing process is accelerated. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors are determinants of the healing process.
Treatment
Sports injuries can be treated and managed by using the P.R.I.C.E.S… DR. ABC, and T.O.T.A.P.S regimes:
| P – Protect R – Rest I – Ice C – Compression E – Elevation S – Stabilize | D – Danger R – Response | A – Airway B – Breathing C – Circulation | T – Talk O – Observe T – Touch A – Active movement P – Passive movement S – Skills test |
The primary inflammatory stage typically lasts around 5 days and all treatment during this time is designed to address the cardinal signs of inflammation – pain, swelling, redness, heat, and a loss of function. Compression sportswear is becoming very popular with both professional and amateur athletes. These garments are thought to both reduce the risk of muscle injury and speed up muscle recovery.
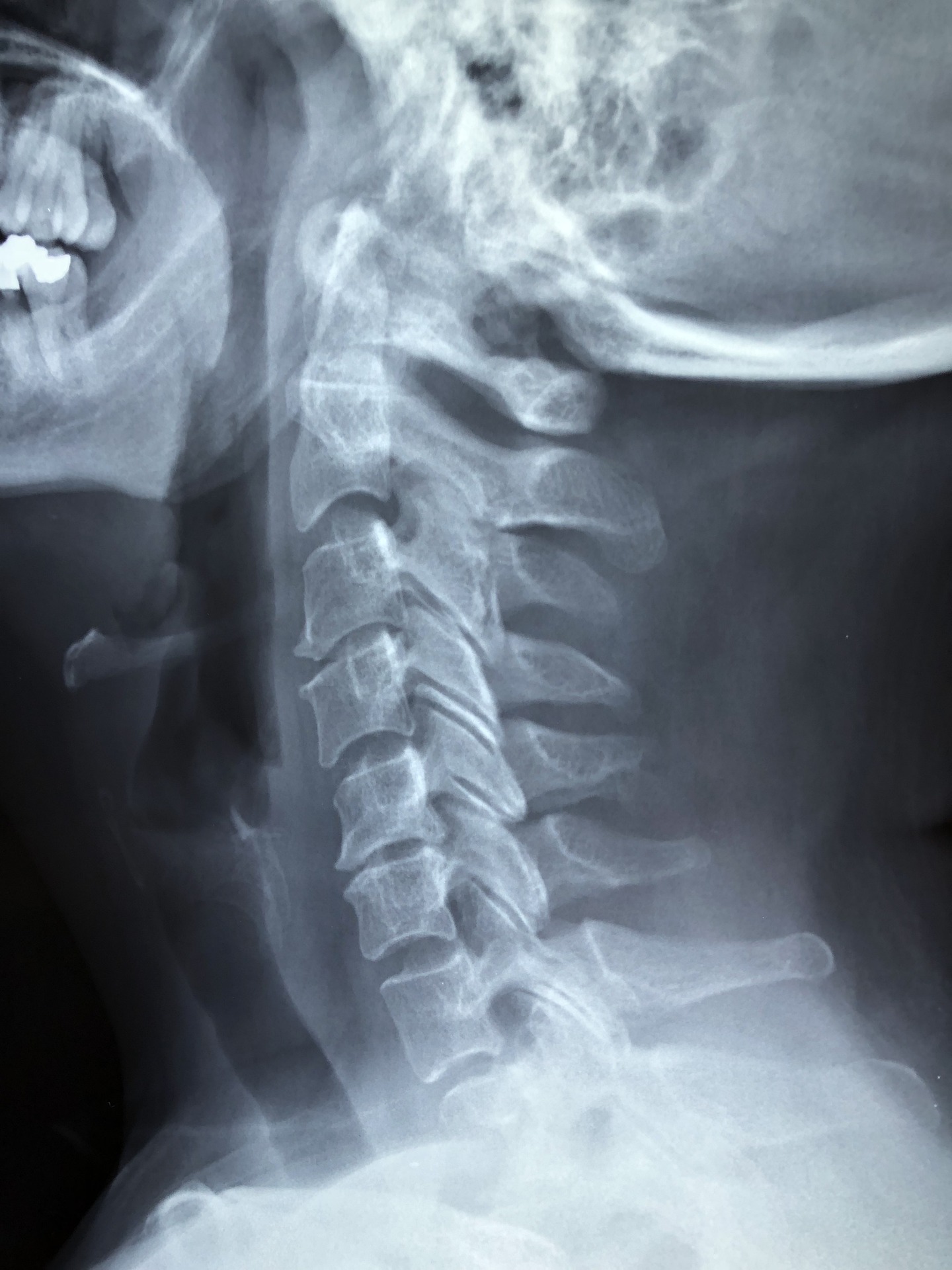
X-Ray
It is common for a doctor to take on X-ray of their patients so that they may get an inside look to see with is going on with their patient’s bone structure, including the spine and its surrounding skeletal structure. Using the information provided from an X-ray, the doctor can see any current irregularities with the spine that may need to be addressed and will also let them know if any further insight needs to be taken, such as through the use of an MRI.
Rehabilitation
Through the use of various stretches and exercises, rehabilitation is used to strengthen the parts of the body that influence posture and movement. It is through practicing rehabilitation that we aim to correct poor posture and imbalanced movements in a way that completely resolves the problem as well as minimizes the chance of their reoccurring in the future.
Exercise Programs
The practice of exercise, both cardiovascular and muscle strengthening, is, coupled with regular chiropractic care, an immensely important aid to managing lower back pain. Exercise promotes maintaining properly toned muscles, better circulation, and healthy digestion. There is strong evidence supporting that exercise is nearly as effective as all other non-surgical treatments in the relief and treatment of lower back pain.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a set of symptoms including pain caused by general compression or irritation of one of five spinal nerve roots of each sciatic nerve—or by compression or irritation of the left or right or both sciatic nerves. Symptoms include lower back pain, buttock pain, and pain, numbness, or weakness in various parts of the leg and foot. Other symptoms include a “pins and needles” sensation, or tingling and difficulty moving or controlling the leg. Typically, symptoms only manifest on one side of the body. The pain may radiate below the knee but does not always.
Sciatica is a relatively common form of low back and leg pain, but the true meaning of the term is often misunderstood. Sciatica is a set of symptoms rather than a diagnosis for what is irritating the root of the nerve to cause the pain. Treatment for sciatica or sciatic symptoms often differs, depending on underlying causes and pain levels. Causes include compression of the sciatic nerve roots by a herniated (torn) or protruding disc in the lower back.
Spinal disc herniation pressing on one of the lumbar or sacral nerve roots is the primary cause of sciatica, being present in about 90% of cases.
Sciatica caused by pressure from a disc herniation and swelling of surrounding tissue can spontaneously subside if the tear in the disc heals and the pulposus extrusion and inflammation cease.
Evidence suggests that spinal manipulation is an effective treatment for acute sciatica.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is caused by the entrapment of the median nerve in the wrist then causes paresthesia, pain, numbness, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve. It appears to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the predisposing factors include diabetes, obesity, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and heavy manual work or work with vibrating tools. The main symptom of CTS is intermittent numbness of the thumb, index, long and radial half of the ring finger. Long-standing CTS leads to permanent nerve damage with constant numbness, atrophy of some of the muscles of the thenar eminence, and weakness of palmar abduction.
The relationship between work and CTS is controversial; in many locations, workers diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome are entitled to time off and compensation. In the USA, carpal tunnel syndrome results in an average of $30,000 in lifetime costs (medical bills and lost time from work). Some speculate that carpal tunnel syndrome is provoked by repetitive movement and manipulating activities and that the exposure can be cumulative. It has also been stated that symptoms are commonly exacerbated by forceful and repetitive use of the hand and wrists in industrial occupations.
Suggested healthy habits such as avoiding repetitive stress, work modification through the use of ergonomic equipment (wrist rest, mouse pad), taking proper breaks, using keyboard alternatives (digital pen, voice recognition, and dictation), and employing early treatments such as taking turmeric (anti-inflammatory), omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins have been proposed as methods to help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
Headaches/Migraines
Nearly 15% of people who make chiropractic visits do so because they suffer from migraines and chronic headaches. During a given year, 90% of people suffer from headaches. Only 1% of headaches seen in the ER have any serious underlying problem. Most reported headaches are caused by tension. Pain can range from mild throbbing pain to unrelenting agony. There are many different sources for headaches, some of which include: stress, overexposure to bright lights, fluctuation in blood sugar, and overexertion in exercise.
Recent studies show that long-term chiropractic care can provide benefits to patients suffering from headaches and migraines greater than that of just using drug therapy. Chiropractic treatment has been shown to be especially effective in providing relief to patients suffering from headaches that originate in the neck or cervical area. According to a study conducted by Duke University in 2001, spinal manipulation provided by chiropractic treatment had great results providing patients with immense relief and leaving them less likely to experience side effects than if they had used medication.
Neck Pain
Neck pain, although felt in the neck, can be caused by numerous other spinal problems. Neck pain may arise due to muscular tightness in both the neck and upper back, or pinching of the nerves emanating from the cervical vertebrae. Joint disruption in the neck creates pain, as does joint disruption in the upper back. Two-thirds of the population will suffer from neck pain at some point in their lives.
The most common causes of neck pain include:
- Stress
- Prolonged postures
- Minor injuries and falls
- Referred pain
- Over-use
- Whiplash
- Herniated disc
- Pinched nerve